Government Initiatives fueling India's Electric Vehicle Expansion
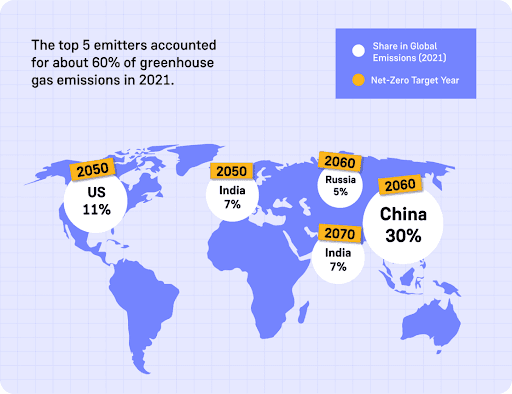
With a rapidly growing population and robust industrial base, India has emerged as one of the world's leading contributors to Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions. While this has a profound impact on the country’s air quality, public health, and environment, it also serves as a reminder that today's choices are already shaping tomorrow's world.
To foster a cleaner and greener future, India is transitioning towards electrifying its transport sector, to reduce GHG emissions. In this context, the adoption of electric vehicles is not just an ambition, but an integral part of sustainable development.
Owing to this, in 2021, India pledged to achieve Net Zero Carbon Emissions by 2070.
Building on this ambitious vision, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways set a target with the EV30@2030 initiative, which by 2030, aims to have:
- 30% of newly registered electric private cars
- 40% of electric buses
- 70% of electric commercial vehicles
- 80% of electric two-wheelers and three-wheelers
This shift goes beyond merely reducing emissions but aims to transform the entire transportation ecosystem.
With significant investments in charging infrastructure, incentives for manufacturers, and supportive policies for consumers, India is poised to lead the global transition to sustainable transportation, with a range of initiatives:
1️. National Mission for Electric Mobility (NMEM) 2011:
This government initiative aims to promote the adoption and manufacturing of electric and hybrid vehicles in the country, reduce dependence on fossil fuels, and promote sustainable transportation.
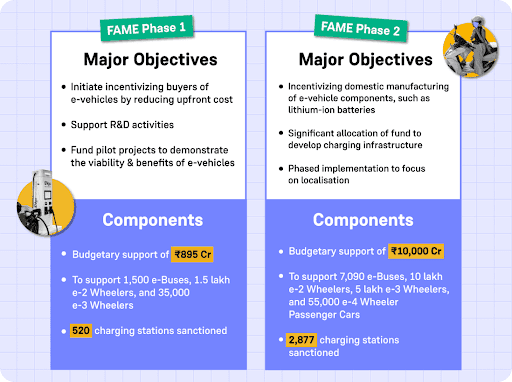
To achieve the goals of NMEM, the National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) 2013 was developed, and the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME) India Scheme was introduced:
- FAME I was launched on April 1, 2015
- FAME II was launched on April 1, 2019
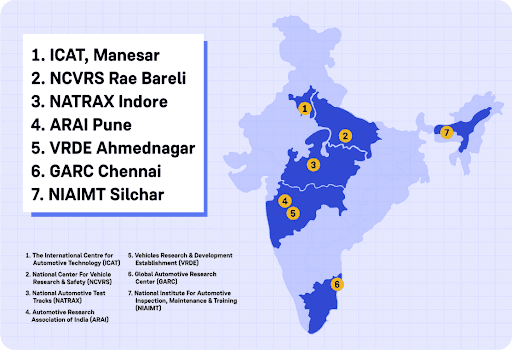
2️. National Automotive Testing and R&D Infrastructure Project (NATRiP):
This project aims to set up 7 state-of-the-art automotive testing and R&D centres across the country, to:
- Foster R&D in the automotive sector, and drive innovation and technological advancements.
- Facilitate compliance with national and international standards for vehicle safety, emissions, and performance.
3. Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes:
- National Program on Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) Battery Storage 2021: With a budget of ₹18,100 Cr, this scheme aims to enhance the manufacturing capacity of ACC batteries up to 50 Gigawatt Hour (GWh), which are primarily used in Electric Vehicle production.
- Automobile and Auto Components 2021: Over 5 years and with ₹25,938 Cr, this scheme aims to boost domestic manufacturing within the automotive and auto components sectors, to position India as a prominent global manufacturing hub.
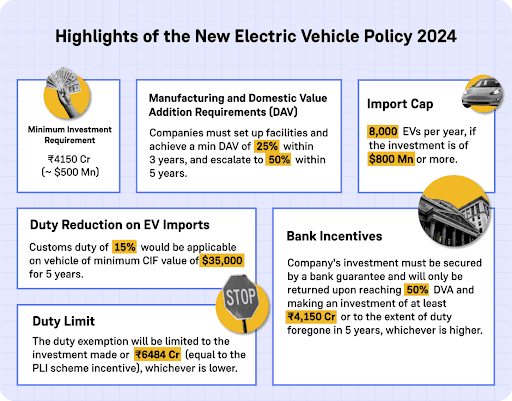
4. ️New Electric Vehicle Policy 2024:
This policy has been specifically designed to attract investment in the e-vehicle space, from renowned global Electric Vehicle manufacturers.
As we look ahead to the ambitious goals of EV30@2030 and the various government policies aimed at accelerating the transition to electric vehicles, it is evident that India is at a pivotal point in shaping the future of transportation.